Abstract
First of all, I want to introduce LS Cable briefly. LG-Cable
changes the name of company to LS-Cable because the ownership
of company is changed in 2005. LS Cable produces not only
cables but also various products like heat pipe, refrigerator,
injection machine, etc. Since 2001, LS Cable has tried to enhance
R&D processes and manufacturing processes by applying TRIZ.
Therefore, LS Cable opened TRIZ education course and have
taught full process of TRIZ to research engineers. And TRIZ has
been adapted to practical engineering projects.
Several successful results were achieved through co-work with
TRIZ team and research engineers. For instance, the quality of
Polymer Insulator and Heat Shrinkable Tube were improved
dramatically. The tolerance of Heat Shrinkable Tube was
relatively more than 10mm and the production speed was limited
by the tolerance. Some solutions which satisfy production speed
and quality were developed by TRIZ. And the tensile strength of
Polymer Insulator was increased by TRIZ, too.
In this paper, TRIZ applications and activities in LS Cable will
be discussed with example of Heat Shrinkable Tube and full
processes.
1. Introduction
LS-Cable, which was one of LG group, was founded in 1962.
Originally it was a company which produce and sell cable or wire,
but today LS-Cable produce lots of product not only cable, but also
tractor, air-conditioning system, small heat pipe in machinery
division, and Li-ion battery, polymer switch in component division.
Business environment of 21 centuries is always changing rapidly,
and the company which evolutes fast can only survive in these
severe competitions.
What is the key point to survive in the worldwide competitions?
In the past, the company which makes the same product at the lower
cost can be successful. Nowadays the company which makes new
paradigm can hold a dominant position.
To make new paradigm, lots of companies put their money to
enhance and to improve R&D process more effectively.
LS-cable noticed that TRIZ can help the research engineers solve
engineering problems and generate new concepts. LS-cable noticed
that there are some differences between TRIZ and other design or
optimization methods. TRIZ is not the methods for quality
management or optimization. It is a method for changing existing
system to other system. TRIZ is very strong methods for generating
new concept and system. Figure 1 is the conventional process to
develop solution in the past, and Figure 2 is TRIZ method for
guiding right solution of engineering problems.
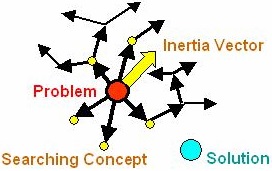
Figure 1. Methods are based on Trial and Error approach
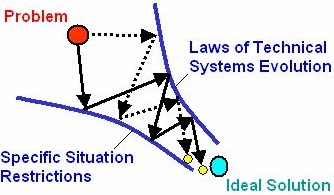
Figure 2. TRIZ directs a problem to Ideal Solution
2. TRIZ History and Process in LS-Cable
In 2001, LS-Cable introduced TRIZ to the research engineers and
in 2002 two TRIZ experts are invited from LG-electronics, and they
carried out 3 projects.
During co-work with them, they suggested several good concepts
which can solve the engineering problem.
In 2003, LS-cable decided to invite a Russian TRIZ expert to
spread TRIZ and adapt to the research engineers. Since 2003, 12
research engineers have graduated 96 hours TRIZ course with their
project to be a TRIZ solver, and 16 projects were done by using
TRIZ. And about 17 patents are made through this co-work with
TRIZ team.
From 2003 to 2004, LS-Cable’s TRIZ activities have been
focused on supporting individual projects. TRIZ team carried out 13
projects and has made 20 patents. In LS-Cable, the TRIZ projects
are usually selected by both engineers and project leaders. Some of
engineers visit TRIZ team to discuss their engineering problem, if
the problem needs kind of computational analysis or optimization
(not suitable to TRIZ), TRIZ team pass the problem to
computational simulation team.
Anyway, there are usually 4 types of engineering problems.
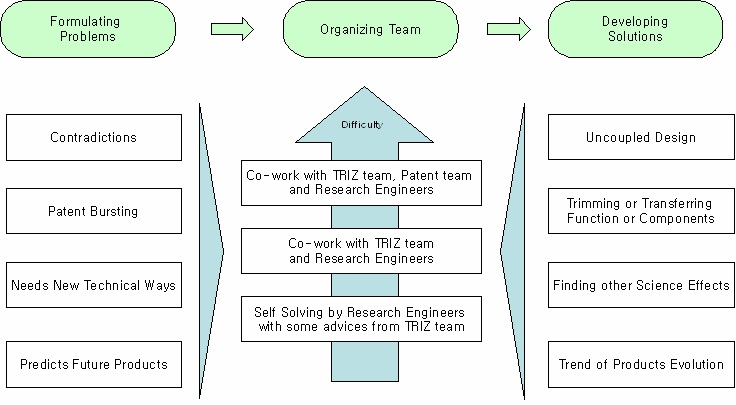
Figure 3. TRIZ process of LS-Cable
In Figure 3, the TRIZ process of LS-Cable is shown. After
formulating engineering problem by discussion with research
engineer, the level of problem difficulty is set. If the problem needs
some of information search, TRIZ team suggested that the research
engineer uses TRIZ software and patent analyzing system. In case
of the problem which has strong contradiction, TRIZ team and
researchers start to co-work for solving problems. In the case of
avoiding patents, TRIZ team, researchers, and patent team help each
other and share information to develop new methods.
But there are several problems only to support engineering projects.
There are saying “Give a man a fish and you feed him for one day.
Teach the people to fish and you feed them for all time”
Only giving idea cannot help them to use TRIZ continuously.
After finishing co-work, they didn’t use TRIZ because TRIZ team
only gave them ideas.
In 2005, LS-Cable decided to build infrastructure in the research
center to spread TRIZ. And TRIZ S/W introduction course was done
to all research engineers.
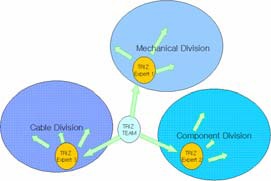
To spread TRIZ and build infrastructure, LS-TRIZ team noticed
that training several TRIZ experts in the company can be effective
way to spread TRIZ as shown in Figure 4.
|
~2004
|
~2005
|
Figure 4. 2005 plan for building Infrastructure in LS-Cable
During S/W education, survey about TRIZ was investigated and
LS-TRIZ team came to know their needs. After that, TRIZ-team
classified every project in the company according to the level and
type of engineering problem of each projects. In 2005, LS-Cable
will establish infrastructure of TRIZ and support the engineers who
want to be TRIZ-experts.
3. Case Study; Introduction of Heat Shrinkable Tube
Since 2001, some of projects show that it is possible to make
successful result by applying TRIZ. The project of improving the
quality of Heat Shrinkable Tube is one of the successful examples.
Heat Shrinkable Tube is a rubber tube which is usually used for
insulating wire connection area. Because it memorizes its original
diameter, it shrinks in a second when thermal energy is applied as
shown Figure 5.

Figure 5. Heat Shrinkable Tube
First of all, we have to analyze engineering system to find
technical problem. Usually functional analysis is used for finding
problems.
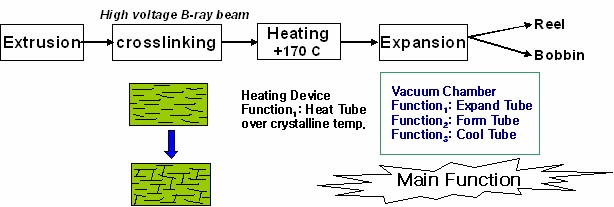
Figure 6. Process of Heat Shrinkable Tube manufacturing
The process which makes Heat Shrinkable Tube is shown in
Figure 6. At first, the original tube is heated over 170’C and is
introduced into the expansion pipe which make tube expanded.
After Expanding, the tube is cooled rapidly because the surface of
tube contacts to the wall of expansion pipe as shown in Figure 7.
During the process, shape memory effect is generated in the tube
like figure 8. It is easy to think that there are some springs inside
Heat Shrinkable Tube.

Figure 7. The Process of Expanding Heat Shrinkable Tube
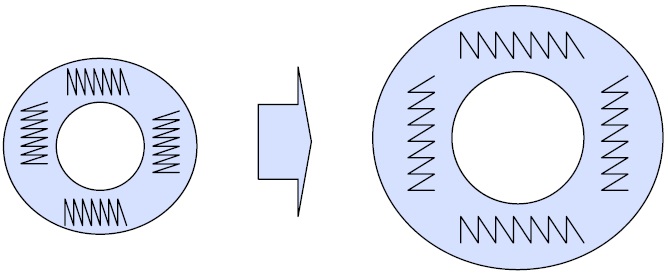
Figure 8. Springs inside of Heat Shrinkable Tube elongated
At that time, the engineers want to increase the speed of
producing Heat Shrinkable Tube. But when the speed of process is
increasing, the longitudinal elongations of Heat Shrinkable Tube
become more irregular after shrinking.
Even though the Heat Shrinkable Tube is cut into the same length,
after shrinking the length of each part becomes different because the
elongation during expansion process is different. In this case it can’t
insulate the electronic component. Figure 9 shows the problem of
heat shrinkable tube.

Figure 9. Irregular Longitudinal Extension of Heat Shrinkable Tube
During rapid expansion inside the expansion pipe, friction is
generated between tube and the wall of expansion pipe. Also
vacuum is applied inside of expansion pipe. The pressure is not
stable. Cooling is also important to decrease time for longitudinal
elongations. Figure 10 shows several estimated reason of problem.
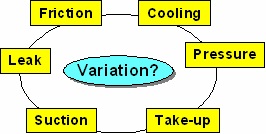
Figure 10. Estimated Source of Problem
Customers of LS-Cable wanted to buy Heat shrinkable Tube
which has more regular elongation change. The researchers tried to
improve the problem by changing only some of parameters, for
example, using colder water to enhance cooling of expansion pipe,
trying to stabilize vacuum pressure, Teflon coating inside of
expansion pipe or putting oil to reduce friction (Figure 11). But they
were not so effective and generate several undesirable effects.
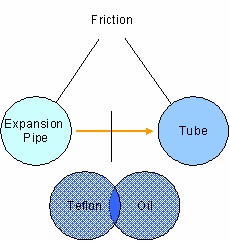
Figure 11.Past Trial to Solve Problem
TRIZ team started to co-work to improve the quality of Heat
Shrinkable Tube. At first, TRIZ team formulates the initial situation
and problem modeling as shown in Figure 12.
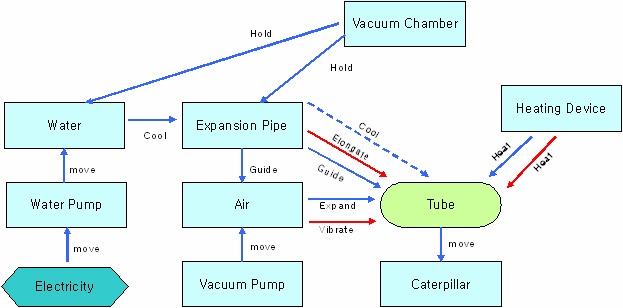
Figure 12.Brief Function Modeling of Expansion Pipe
4. Case Study: Developing New Concepts for Shrinkable Tube
During formulating Problems, some contradictions are derived
from analysis. Using this problem modeling, more than 10 concepts
were generated to solve the tube’s irregular elongation problem.
At first, TRIZ team found technical contradiction between
expansion pipe and Heat Shrinkable Tube. If the speed of
production gets faster and faster, the longitudinal elongation became
bigger. Figure 13 shows technical contradiction and recommended
inventive principles.
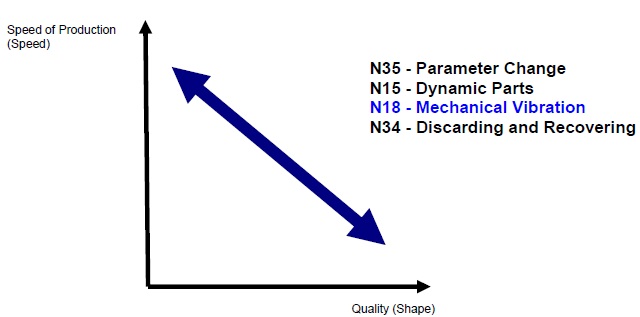
Figure 13. Technical Contradiction of the system
To reduce friction between expansion pipe and Heat Shrinkable
Tube, mechanical vibration for reducing friction is suggested, but it
needs more cost and device. It increases complexity of technical
system, so this method couldn’t be used.
TRIZ team focused on one of the contradictions and it was also a
psychological inertia. The contradiction was that the tube should be
hot and cold, which is physical contradiction.
If the tube is cold, no elongation is occurred in the Heat
Shrinkable tube, but the tube can not be expanded. Engineers
thought that the tube must not be cold to make expansion process.
TRIZ team found a similar problem and solution in the other
area’s examples. It was a pressing and bending process for plate.
In Figure 14, It needs over 1200oC temperature to bend the plate
by press, but over 800oC the plate is oxidized. This problem needs
high and low temperature at the same time.
To solve the contradiction, the engineers of the press area used
surface cooling method. The plate can be bended because the plate
is over 1200oC on the whole, and it is not oxidized because the area
which meets air is below 800oC.
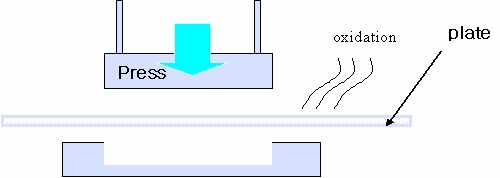
Figure 14. Prevent oxidization during pressing
TRIZ team decided to import the method into expansion pipe
system. First of all, the operating time and operating zone were
checked. Operating time means the duration time of tube in the
expansion pipe.
- operating zone : surface of tube
- operating time : 0.01sec
TRIZ team and research engineers decided that the method of
pressing plate without oxidation can be used to reduce the irregular
elongation of Heat Shrinkable Tube.
To make similar effect, new design of expansion pipe is
suggested in Figure 15.
Like pressing process, if only surface of tube is cooled, the skin
is hardened and it can resist the friction between the wall and tube
as shown in Figure 16. It makes little elongation of tube during
expansion. On the whole, because the tube is hot, the tube can be
expanded easily.
To make surface hard, peltier cooler is applied in the upper area
of the expansion pipe, because air or metal pipe surface with water
cooling was not sufficient for cooling surface of tube. This peltier
cooling system is usually used for small cooling system like water
purifier.
Robust tube is gained through this method and the
longitudinal elongation of Heat Shrinkable Tube is decreased.
Before applying TRIZ, the engineer only focused on changing
parameters of some components of this system. After applying TRIZ,
it is revealed that changing product is also possible way.

Figure15. Expansion pipe with peltier cooler

Figure16. Hardened Skin can prevent elongation
The longitudinal tolerance of conventional Heat Shrinkable Tube
was 10 mm. After using peltier cooler on the top of the expansion
pipe, and the tolerance reduced to 5mm per 100 mm of length. The
quality of Heat Shrinkable Tube was improved.
5. Conclusion
The case study shown in this paper is one of the examples which
are applied in real engineering problem in LS-Cable. Since TRIZ is
introduced in LS-Cable in 2001, TRIZ is promoted actively in LSCable.
In 2005, LS-Cable will focus on making infrastructure of TRIZ
to spread TRIZ more effectively, and will apply TRIZ to various
area. With co-work with research engineer and patent analysis team,
it is expected that synergy effect for improving R&D process will be
generated.
6. References
- Genrich Altshuller, 1997, 40 Principles, Technical Innovation
Center.
- Young-Ju Kang, Alexander Skuratovich, Pyeong-Kwan Chung,
2004, "TRIZ applied to Axiomatic Design, and case study;
improving tensile strength of polymer insulator", ETRIA 2004
Conference Proceedings, Nov 3-5.
- Genrich Altshuller, 1996, And Suddenly the Inventor Appeared:
TRIZ, the Theory of Inventive Problem Solving, Technical
Innovation Center.
| 

















 ââåðõ
ââåðõ